Decision-Making Bias – What, Me Worry?
RFG POV: The results of decision-making bias can come back to bite you. Decision-making bias exists and is challenging to eliminate! In my last post, I discussed the thesis put forward by Nobel Laureate Daniel Kahneman and co-authors Dan Lovallo, and Olivier Sibony in their June 2011 Harvard Business Review (HBR) article entitled "Before You Make That Big Decision…". With the right HBR subscription you can read the original article here. Executives must find and neutralize decision-making bias.
The authors discuss the impossibility of identifying and eliminating decision-making bias in ourselves, but leave open the door to finding decision-making bias in our processes and in our organization. Even better, beyond detecting bias you may be able to compensate for it and make sounder decisions as a result. Kahneman and his McKinsey and Co. co-authors state:
We may not be able to control our own intuition, but we can apply rational thought to detect others' faulty intuition and improve their judgment.
Take a systematic approach to decision-making bias detection and correction
The authors suggest a systematic approach to detecting decision-making bias. They distill their thinking into a dozen rules to apply when taking important decisions based on recommendations of others. The authors are not alone in their thinking!
In an earlier post on critical thinking, I mentioned the Baloney Detection Kit. You can find the "Baloney Detection Kit" for grown-ups from the Richard Dawkins Foundation for Reason and Science and Skeptic Magazine editor Dr. Michael Shermer on the Brainpickings.org website, along with a great video on the subject.
Decision-making Bias Detection and Baloney Detection
How similar are Decision-bias Detection and Baloney Detection? You can judge for yourself by looking at the table following. I’ve put each list in the order that it was originally presented, and made no attempt to cross-reference the entries. Yet it is easy to see the common threads of skepticism and inquiry. It is all about asking good questions, and anticipating familiar patterns of biased thought. Of course, basing the analysis on good quality data is critical!
Decision-Bias Detection and Baloney Detection Side by Side
|
Decision-Bias Detection
|
Baloney Detection
|
|---|---|
| Is there any reason to suspect errors driven by your team's self-interest? | How reliable is the source of the claim |
| Have the people making the decision fallen in love with it? | Does the source of the claim make similar claims? |
| Were there any dissenting opinions on the team? | Have the claims been verified by someone else (other than the claimant?) |
| Could the diagnosis of the situation be overly influenced by salient analogies? | Does this claim fit with the way the world works? |
| Have credible alternatives been considered? | Has anyone tried to disprove the claim? |
| If you had to make this decision again in a year, what information would you want, and can you get more of it now? | Where does the preponderance of the evidence point? |
| Do you know where the numbers came from | Is the claimant playing by the rules of science? |
| Can you see the "Halo" effect? (the story seems simpler and more emotional than it really is." | Is the claimant providing positive evidence? |
| Are the people making the recommendation overly attached to past decisions? | Does the new theory account for as many phenomena as the old theory? |
| Is the base case overly optimistic? | Are personal beliefs driving the claim? |
| Is the worst case bad enough? | ---------------------------- |
| Is the recommending team overly cautious? | ---------------------------- |
Conclusion
While I have blogged about the negative business outcomes due to poor data quality, good quality data alone will not save you from the decision-making bias of your recommendations team. When good-quality data is miss-applied or miss-interpreted, absent from the decision-making process, or ignored due to personal "gut" feelings, decision-making bias is right there, ready to bite you Stay alert, and stay skeptical!
reprinted by permission of Stu Selip, Principal Consulting LLC
Cisco, Dell and Economic Impacts
Lead Analyst: Cal Braunstein
Cisco Systems Inc. reported respectable financial results for its fourth quarter and full year 2013 but plans on layoffs nonetheless. Meanwhile, Dell Inc. announced flat second quarter 2104 results, with gains in its enterprise solutions and services that were offset by declines in end user computing revenues. In other news, recession has ended in the EU but U.S. and global growth weak.
Focal Points:
• Cisco, a bellwether for IT and the global economy overall, delivered decent fourth quarter and fiscal year 2013 financial results. For the quarter Cisco had revenues of $12.4 billion, an increase of 6.2 percent over the previous year's quarter. Net income on a GAAP basis was $2.3 billion for the quarter, an 18 percent jump year-over-year. For the full fiscal year Cisco reported revenues of $48.6 billion, up 5.5 percent from the prior year while net income for the year on a GAAP basis was $10.0 billion, a 24 percent leap from the 2012 fiscal year. The company plans on laying off 4,000 employees – or about five percent of its workforce – beginning this quarter due to economic uncertainty. According to CEO John Chambers the economy is "more mixed and unpredictable than I have ever seen it." While he sees growth in the public sector for a change, slow growth in the BRIC (Brazil, Russia, India, China) nations, EU, and U.S. are creating headwinds, he claims. On the positive front, Chambers asserts Cisco is number one in clouds and major movements in mobility and the "Internet of everything" will enable Cisco to maintain its growth momentum.
• Dell's second quarter revenues were $14.5 billion, virtually unchanged from the previous year's quarter. Net income on a GAAP basis was $433 million, a drop of 51 percent year-over-year. The Enterprise Solutions Group (ESG) achieved an eight percent year-over-year growth while the Services unit grew slightly and the predominant End User Computing unit shrank by five percent. The storage component of ESG declined by 7 percent and is now only 13 percent of the group's revenues. The server, networking, and peripherals component of ESG increased its revenues by 10 percent, with servers doing well and networking up 19 percent year-over-year. Dell claims its differentiated strategy includes a superior relationship model but that has not translated to increased services revenues. Dell's desktop and thin client revenues were flat year-over-year while mobility revenues slumped 10 percent and software and peripherals slid five percent in the same period. From a geographic perspective, the only newsworthy revenue gains or losses occurred in the BRIC countries. Brazil and India were up seven and six percent, respectively, while China was flat and Russia revenue collapsed by 33 percent from the previous year's quarter.
• Second quarter saw an improved outlook in Europe. It was reported that Eurozone GDP rose 0.3 percent, the first positive-territory reading for the Union since late 2011. Portugal surprised everyone with a 1.1 percent GDP jump while France and Germany grew 0.5 percent and 0.7 percent, respectively. Meanwhile, the U.S. economy grew 1.7 percent in the second quarter. According to the revisions, U.S. GDP growth nearly stalled at 0.1 percent in the fourth quarter of 2012, and rose 1.1 percent in the first quarter of this year (versus the estimated 1.8 percent). Additionally, venture capital has slipped 7 percent this year.
RFG POV: Cisco's financial results and actions can be viewed as a beacon of what businesses and IT executives can expect to encounter over the near term. The economic indicators are hinting at a change of leadership and potential problems ahead in some unexpected areas. The BRIC nations are running into headwinds that may not abate soon but may even get much worse, according to some economists. The U.S. GDP growth is flattening again for the third straight second half of the year and the EU, while improving, has a long way to go before it becomes healthy. This does not bode well for IT budgets heading into 2014 or for hiring. IT executives will need to continue transforming their operations and find ways to incorporate new, disruptive technologies to cut costs and improve productivity. As the Borg of Star Trek liked to say "resistance is futile." While transformation is a multi-year initiative, IT executives that do not move rapidly to cost-efficient "IT as a Service" environments may find they have put their organizations and themselves at risk.
System Dynamics is now for the rest of us!
by Stu Selip, Principal Consulting
That's great, but what is it? According to the System Dynamics Society
System dynamics is a computer-aided approach to policy analysis and design. It applies to dynamic problems arising in complex social, managerial, economic, or ecological systems -- literally any dynamic systems characterized by interdependence, mutual interaction, information feedback, and circular causalitySo, System Dynamics (SD) uses computers to simulate dynamic systems that are familiar to us in the realms of business and technology. OK that sounds great, but why am I writing about SD? A presentation by ViaSim Solution's (ViaSim) president J. Chris White and his ViaSim colleague Robert Sholtes at last Friday's InfoGov Community call piqued my interest, and I think SD will pique your interest too.
What do the big guys do with SD?
 Chris and Robert mentioned the long-time application of SD in the Department of Defense (DOD). A quick Google search revealed widespread use ranging from scholarly articles about simulating the control behavior of fighter planes to pragmatic approaches to re-architecting the acquisition process of the DOD itself. It looks like the DOD appreciates System Dynamics. Here is a clip from that search. Large enterprises can make good use of SD too. In a 2008 Harvard Business Review (HBR) article entitled Mastering the Management System by Robert S. Kaplan and David P. Norton, the authors identify the concept of closed loop management systems in linking strategy with operations, informed by feedback from operational results.
Chris and Robert mentioned the long-time application of SD in the Department of Defense (DOD). A quick Google search revealed widespread use ranging from scholarly articles about simulating the control behavior of fighter planes to pragmatic approaches to re-architecting the acquisition process of the DOD itself. It looks like the DOD appreciates System Dynamics. Here is a clip from that search. Large enterprises can make good use of SD too. In a 2008 Harvard Business Review (HBR) article entitled Mastering the Management System by Robert S. Kaplan and David P. Norton, the authors identify the concept of closed loop management systems in linking strategy with operations, informed by feedback from operational results.
Various studies done in the past 25 years indicate that 60% to 80% of companies fall short of the success predicted from their new strategies. By creating a closed-loop management system, companies can avoid such shortfalls.Their article, which you can see here with the right HBR subscription, discusses how this might be done, without explicitly mentioning System Dynamics.
What about the rest of us?
Most of the rest of us are involved in more mundane tasks than articulating corporate strategy. Many of us work on planning IT projects, with plans defined in Microsoft Project (MSP). How many MSP users have solid training in the tool? I'll wager that many practitioners have learned MSP by the "seat of their pants", never quite understanding why a small change to the options of a project plan has produced dramatically different timelines, or why subtle changes cause plans to oscillate between wildly optimistic, and depressingly pessimistic. 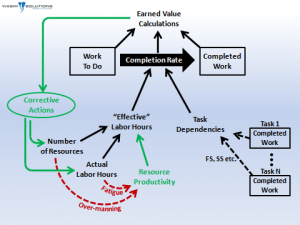 The ViaSim team spoke directly to these points by introducing us to pmBLOX, an SD-empowered MSP-like project planning tool that addresses MSP issues that cause us to lose confidence and lose heart. In this graphic, developed by ViaSim, the black arrows indicate inputs normally available to MSP users. The key differences are shown in the green and red arrows. With pmBLOX, project planners may specify corrective actions like adding workers to projects that are challenged. In addition, project planners can account for project delivery inefficiencies resulting from fatigue, or excessive staffing. You can watch Chris explain this himself, right here. At last, we will be able to respect Brook's Law, the central thesis of which is "adding manpower to a late software project makes it later". Dr. Fred Brooks expanded on this at length in The Mythical Man-Month, published by Addison Wesley in 1975. When I asked Chris about his experience with the challenges of mythical man-month project planning and non-SD project planning solutions he told me
The ViaSim team spoke directly to these points by introducing us to pmBLOX, an SD-empowered MSP-like project planning tool that addresses MSP issues that cause us to lose confidence and lose heart. In this graphic, developed by ViaSim, the black arrows indicate inputs normally available to MSP users. The key differences are shown in the green and red arrows. With pmBLOX, project planners may specify corrective actions like adding workers to projects that are challenged. In addition, project planners can account for project delivery inefficiencies resulting from fatigue, or excessive staffing. You can watch Chris explain this himself, right here. At last, we will be able to respect Brook's Law, the central thesis of which is "adding manpower to a late software project makes it later". Dr. Fred Brooks expanded on this at length in The Mythical Man-Month, published by Addison Wesley in 1975. When I asked Chris about his experience with the challenges of mythical man-month project planning and non-SD project planning solutions he told me
As we often see in the real world, sometimes "throwing people" at the problem puts the project further behind schedule. With these real-world corrective actions and productivity impacts, pmBLOX provides a framework for creating realistic and achievable plans. The biggest risk for any project is to start with an unrealistic baseline, which is often the case with many of today's simple (yet popular) project planning tools.
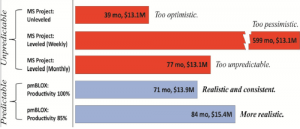 Here is an example of the output of MSP and the output of pmBLOX for an actual DOD project. You can see how a minor change in an MSP setting (leveling) made some dramatic and scary changes in the project plan. Notice that the output of pmBLOX looks much more realistic and stable with respect to project plan changes.
Here is an example of the output of MSP and the output of pmBLOX for an actual DOD project. You can see how a minor change in an MSP setting (leveling) made some dramatic and scary changes in the project plan. Notice that the output of pmBLOX looks much more realistic and stable with respect to project plan changes.
What about the learning curve for pmBLOX?
There is good news here. pmBLOX designers adopted the MSP paradigm and allow for direct importing of existing MSP-based plans. Here is an example of how pmBLOX looks,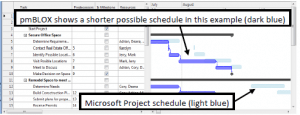 and how it depicts the difference between its plan and the one suggested by MSP. To my eye, the interface is familiar, so adopting and transitioning to pmBLOX should not be very difficult.
and how it depicts the difference between its plan and the one suggested by MSP. To my eye, the interface is familiar, so adopting and transitioning to pmBLOX should not be very difficult.
RFG POV:
System Dynamics (SD) is a powerful simulation approach for dynamic systems and pmBLOX puts some of that SD-power into the hands of project planners. While the ViaSim presenters talked about much more than pmBLOX, I thought the project management paradigm would make a good introduction point for discussing this interesting technology. In September, the ViaSim team will present again at an InfoGov Community call. At that meeting they will, among other topics, address how SD simulations are tested to give SD developers and users confidence in the results of their simulations. If you are an InfoGov member, you will want to attend. If you are not yet an InfoGov member, consider joining.
-The Little Mainframe That Could
RFG Perspective: The just-launched IBM Corp. zEnterprise BC12 servers are very competitive mainframes that should be attractive to organizations with revenues in excess of, or expanding to, $100 million. The entry level mainframes that replace last generation's z114 series can consolidate up to 40 virtual servers per core or up to 520 in a single footprint for as low as $1.00 per day per virtual server. RFG projects that the zBC12 ecosystem could be up to 50 percent less expensive than comparable all-x86 distributed environments. IT executives running Java or Linux applications or eager to eliminate duplicative shared-nothing databases should evaluate the zBC12 ecosystem to see if the platform can best meet business and technology requirements.
Contrary to public opinion (and that of competitive hardware vendors) the mainframe is not dead, nor is it dying. In the last 12 months the zEnterprise mainframe servers have extended growth performance for the tenth straight year, according to IBM. The latest MIPS (millions of instructions per second) installed base jumped 23 percent year-over-year and revenues jumped 10 percent. There have been 210 new accounts since the zEnterprise launch as well as 195 zBX units shipped. More than 25 percent of all MIPS are IFLs, specialty engines that run Linux only, and three-fourths of the top 100 zEnterprise customers have IFLs installed. The ISV base continues to grow with more than 7,400 applications available and more than 1,000 schools in 67 countries participate in the IBM Academic Initiative for System z. This is not a dying platform but one gaining ground in an overall stagnant server market. The new zBC12 will enable the mainframe platform to grow further and expand into lower-end markets.
zBC12 Basics
The zBC12 is faster than the z114, using a 4.2GHz 64-bit processor and has twice the maximum memory of the z114 at 498 GB. The zBC12 can be leased starting at $1,965 a month, depending upon the enterprise's credit worthiness, or it can be purchased starting at $75,000. RFG has done multiple TCO studies on the zEnterprise Enterprise Class server ecosystems and estimates the zBC12 ecosystem could be 50 percent less expensive than x86 distributive environments having the equivalent computing power.
On the analytics side, the zBC12 offers the IBM DB2 Analytics Accelerator that IBM says offers significantly faster performance for workloads such as Cognos and SPSS analytics. The zBC12 also attaches to Netezza and PureData for Analytics appliances for integrated, real-time operational analytics.
Cloud, Linux and Other Plays
On the cloud front, IBM is a key contributor to OpenStack, an open and scalable operating system for private and public clouds. OpenStack was initially developed by RackSpace Holdings and currently has a community of more than 190 companies supporting it including Dell Inc., Hewlett-Packard Co. (HP), IBM, and Red Hat Inc. IBM has also added its z/VM Hypervisor and z/VM Operating System APIs for use with OpenStack. By using this framework, public cloud service providers and organizations building out their own private clouds can benefit from zEnterprise advantages such as availability, reliability, scalability, security and costs.
As stated above, Linux now accounts for more than 25 percent of all System z workloads, which can run on zEnterprise systems with IFLs or on a Linux-only system. The standalone Enterprise Linux Server (ELS) uses the z/VM virtualization hypervisor and has available more than 3,000 tested Linux applications. IBM provides a number of specially-priced zEnterprise Solution Editions, including the Cloud-Ready for Linux on System z, which turns the mainframe into an Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) platform. Additionally, the zBC12 comes with EAL5+ security, which satisfies the high levels of protection on a commercial server.
The zBC12 is an ideal candidate for mid-market companies to act as the primary data server platform. RFG believes organizations will save up to 50 percent of their IT ecosystem costs if the mainframe handles all the data serving, since it provides a shared-everything data storage environment. Distributed computing platforms are designed for shared-nothing data storage, which means duplicate databases must be created for each application running in parallel. Thus, if there are a dozen applications using the customer database, then there are 12 copies of the customer file in use simultaneously. These must be kept in sync as best as possible. The costs for all the additional storage and administration can make the distributed solution more costly than the zBC12 for companies with revenues in excess of $100 million. IT executives can architect the systems as ELS only or with a mainframe central processor, IFLs and zBX for Microsoft Corp. Windows applications, depending on the configuration needs.
Summary
The mainframe myths have misled business and IT executives into believing mainframes are expensive and outdated, and led to higher data center costs and sub-optimization for mid-market and larger companies. With the new zEnterprise BC12 IBM has an effective server platform that can counter the myths and provide IT executives with a solution that will help companies contain costs, become more competitive, and assist with a transformation to a consumption-based usage model.
RFG POV: Each server platform is architected to execute certain types of application workloads well. The BC12 is an excellent server solution for applications requiring high availability, reliability, resiliency, scalability, and security. The mainframe handles mixed workloads well, is best of breed at data serving, and can excel in cross-platform management and performance using its IFLs and zBX processors. IT executives should consider the BC12 when evaluating platform choices for analytics, data serving, packaged enterprise applications such as CRM and ERP systems, and Web serving environments.
CEOs CIOs not in Sync
Lead Analyst: Cal Braunstein
According to a post on the Harvard Business Review blog CEOs and CIOs are not in sync when it comes to the new challenges and issues CEOs are facing. Study findings point to the fact that CIOs do not understand where the business needs to go, and CIOs do not have a strategy to address business challenges or opportunities.
Focal Points:
- Key findings from their research are almost half of the CEOs feel IT should be a commodity service purchased as needed. Almost half of the CEOs rate their CIOs negatively in terms of understanding the business and how to apply IT in new ways to the business. Only 25 percent of executives felt their CIOs were performing above their peers. Moreover, 57 percent of CEOs expect their IT function to change significantly over the next three years, while 12 percent predict a "complete overhaul" of IT.
- The above findings are attributed to four trends that are changing the CIOs role. Many CEOs are moving away from ownership and return on assets or investment (ROA or ROI) analyses and are thinking about renting IT equipment for items not directly tied to value creation. The shift from efficiency and scalability to agility and efficacy translates into a movement away from transactional systems to new systems that provide agility, collaboration, and transparency. Thirdly, the boundaries between contractors, channels, customers, partners, staff, suppliers, and even competitors are diminishing and in some cases disappearing, creating a whole new user community for enterprise IT systems. All of this changes how companies manage and organize work and resources, which suggests the need for more unique, niche applications with integration of information and systems across organizational and agent boundaries.
- In summary it states there new systems, business and delivery models, types of information, technologies, and whole new roles for IT in the enterprise's ecosystem. These new business insights, tied to the emergence of new technologies, are creating an opportunity for IT to lead business transformational efforts, creating new business models, initiating new business processes and making the enterprise agile in this challenging economic environment, the report concludes.
RFG POV: Business executives that think IT should be a commodity service purchased as needed do not perceive IT as a business differentiator. That is problematic for their businesses and for IT executives that work for them. IT executives in those organizations need to enlighten the business executives on the flaws in their thinking. As to the four trends identified, RFG and other studies have also found these to be true, which is why RFG has been pushing for IT executives to transform their operations. Business and IT always exist in a state of change, including disruptive innovation, and the next decade will be no different. IT executives must work with business executives to help transform the business and expose them to new process possibilities that are available due to the emerging technologies. IT executives must believe (and pursue) their role is to sell the business – e.g., sell cereal if they work for Kellogg's – and not be a "tech head" if they want a seat at the business table.
Disruptive Changes
Lead Analyst: Cal Braunstein
Amazon Inc. and Microsoft Corp. lowered their pricing for certain cloud offerings in attempts to maintain leadership and/or preserve customers. Similarly, Hewlett-Packard Co. (HP) launched its next-generation Moonshot hyperscale servers. Meanwhile, IDG Connect, the demand generation division of International Data Group (IDG), released its survey findings that show there may be a skills shortage when it comes to the soft skills required when communicating beyond the IT walls.
Focal Points:
- Earlier this month Amazon price reduced the prices it charged for its Windows on-demand servers by up to 26 percent. This brought its pricings within pennies of Microsoft's Windows Azure cloud fees. The price reductions apply across Amazon's standard (m1), second-generation standard (m3), high-memory (m2), and high-CPU (c1) instance families. CEO Jeff Bezos stated in the Amazon annual report the strategy of cutting prices before the company needs to, and developing technologies before there is a financially motivating factor, is what protects the company from unexpected markets shifts. Microsoft has responded by aggressively cutting its prices by 21 to 33 percent for hosting and processing customer online data. In order for customers to qualify for the cuts they must make monthly commitments to Azure for either six or 12 months. Microsoft also is making its Windows Azure Virtual Network technology (codenamed "Brooklyn") generally available effective April 16. Windows Azure Virtual Network is designed to allow companies to extend their networks by enabling secure site-to-site VPN connectivity between the enterprise and the Windows Azure cloud.
- HP launched its initial Moonshot servers, which use Intel Corp. Atom low-cost, low-energy microprocessors, This next-generation of servers is the first wave of hyperscale software defined server computing models to be offered by HP. These particular servers are designed to be used in dedicated hosting and Web front end environments. The company stated that two more "leaps" will be out this year that will be targeted to handle other specific workloads. HP claims its architecture can scale 10:1 over existing offerings while providing eight times the efficiency. The Moonshot 1500 uses Intel Atom S1200 microprocessors, utilizes a 4.3U (7.5 inch tall) chassis that hosts 45 "Gemini" server cartridges, and up to 1800 quad-core servers will fit into a 42U rack. Other x86 chips from Advanced Micro Devices Inc. (AMD), plus ARM processors from Calxeda Inc., Texas Instruments Inc., and Applied Micro Circuits Corp. (AMCC) are also expected to be available in the "Gemini" cartridge form factor. The first Moonshot servers support Linux, but are compatible with Windows, VMware and traditional enterprise applications. Pricing starts at $61,875 for the enclosure, 45 HP ProLiant Moonshot servers and an integrated switch, according to HP officials. (For more on this topic see this week's Research Note "HP's Moonshot – the Launch.")
- According to a new study by IDG Connect, 83 percent of European respondents believe there is no IT skills shortage while 93 percent of U.S. respondents definitely feel there is a gap between the technical skills IT staff possess and the skills needed by the respondents' companies. IDG attributes this glaring differentiation to what are loosely defined as "hard" (true technical skills and competencies) and "soft" (business, behavioral, communications, and interpersonal) skills. The European respondents focused on hard skills while their American counterparts were more concerned about the soft skills, which will become more prevalent within IT as it goes through a transformation to support the next-generation data center environments and greater integration with the business. As IT becomes more integrated with the business and operational skill requirements shift, IDG concludes "companies can only be as good as the individuals that work within them. People … are capable of creative leaps of thinking and greatness that surpass all machines. This means that any discussion on IT skills, and any decision on the qualities required for future progression are fundamental to innovation. This is especially true in IT, where the role of the CIO is rapidly expanding within the enterprise and the department as a whole is becoming increasingly important to the entire business. It seems IT is forever teetering on the brink of bigger and better things - and it is up to the people within it to maximize this potential."
RFG POV: IT always exists in a state of disruptive innovation and the next decade will be no different. Whether it is a shift to the cloud, hyperscale computing, software-defined data center or other technological shifts, IT must be prepared to deal with the business and pricing models that arise. Jeff Bezos is correct by not sitting on his laurels and constantly pushing the envelope in pricing and services. IT executives need to do the same and deliver comparable services at prices that appeal to the business while covering costs. This requires keeping current on technology and having the staff on board that can solve the business problems and deliver innovative solutions that enable the organization to remain competitive. RFG expects the staffing dilemma to emerge over the next few years as data centers transform to meet the next generation of business and IT needs. At that time most IT staff will not need the current skills they use but skills that allow them to work with the business, providers and others to deliver solutions built on logical platforms (rather than physical infrastructure). Only a few staff will need to know the nuts and bolts of the hardware and physical layouts. This paradigm shift in staff capabilities and skills must be anticipated if IT executives do not want to be caught behind the curve and left to struggle with catching up with demand. IT executives should be developing their next-generation IT development and operations strategies, determining skills needed and the gap, and then begin a career planning and weaning-out process so that IT will be able to provide the leadership and skills needed to support the business over the next decade of disruptive innovation. Additionally, IT executives should determine if Moonshot servers are applicable in their current or target environments, and if so, conduct a pilot when the time is right.
Service Delivery to Business Enablement: Data Center Edition
Lead Analyst: Adam Braunstein
I have never been a fan of alarmist claims. Never have I witnessed the sky falling or the oceans abruptly swallowing masses of land. Nonetheless, we have all seen the air become unsafe to breathe in many parts of the world and rising water levels are certainly cause for concern. When rapid changes occur, those progressions do not take place overnight and often require a distanced perspective. Secondly, being paranoid does not mean one is wrong.
Such is the case with the shifts occurring in the data center. Business needs and disruptive technologies are more complex, frequent, and enduring despite their seemingly iterative nature. The gap between the deceptively calm exterior and true nature of internal data center changes threatens to leave IT executives unable to readily adapt to the seismic shifts taking place beneath the surface. Decisions made to address long-term needs are typically made using short-term metrics that mask the underlying movements themselves and the enterprise need to deal strategically with these changes. The failure to look at these issues as a whole will have a negative cascading effect on enterprise readiness in the future and is akin to France's Maginot Line of defense against Germany in World War II. While the fortifications prevented a direct attack, the tactic ignored the other strategic threats including a Belgium-based attack.
Three-Legged Stool: Business, Technology, and Operations
The line between business and technology has blurred such that there is very little difference between the two. The old approach of using technology as a business enabler is no longer valid as IT no longer simply delivers the required business services. Business needs are now so dependent on technology that the planning and execution need to exist using same game plan, analytic tools, and measurements. Changes in one directly impact the other and continuous updates to strategic goals and tactical executions must be carefully weighed as the two move forward together. Business enablement is the new name of the game.
With business and technology successes and failures so closely fused together, it should be abundantly clear why shared goals and execution strategies are required. The new goalposts for efficient, flexible operations are defined in terms of software-defined data centers (SDDCs). Where disruptive technologies including automation, consolidation, orchestration and virtualization were previously the desired end state, SDDCs up the ante by providing logical views of platforms and infrastructures such that services can be spooled up, down, and changed dynamically without the limitations of physical constraints. While technology comprises the underpinnings here, the enablement of dynamic and changing business goals is the required outcome.
Operations practices and employee roles and skills will thus need to rapidly adapt. Metrics like data density, workload types and utilization will remain as baseline indicators but only as a means to more important measurements of agility, readiness, productivity, opportunity and revenue capture. Old technologies will need to be replaced to empower the necessary change, and those new technologies will need to be turned over at more rapid rates to continue to meet the heightened business pace as well as limited budgets. Budgeting and financial models will also need to follow suit.
The Aligned Business/IT Model of the Future: Asking the Right Questions
The fused business/IT future will need to be based around a holistic, evolving set of metrics that incorporate changing business dynamics, technology trends, and performance requirements. Hardware, software, storage, supporting infrastructure, processes, and people must all be evaluated to deliver the required views within and across data centers and into clouds. Moreover, IT executives should incorporate best-of-breed information enterprise data centers in both similar and competing industries.
The set of delivered dashboards should provide a macro view of data center operations with both business and IT outlooks and trending. Analysis should provide the following:
- Benchmark current data center performance with comparative data;
- Demonstrate opportunities for productivity and cost cutting improvements;
- Provide insight as to the best and most cost effective ways to align the data center to be less complex, more scalable, and able to meet future business and technology opportunities;
- Offer facilities to compare different scenarios as customers determine which opportunities best meet their needs.
Even though the reality of SDDCs is years away, IT executives must be travelling on the journey now. There are a number of intermediary milestones that must be achieved first and delays in reaching them will negatively impact the business. Use of data center analytical tools as described above will be needed to help chart the course and monitor progress. (The GreenWay Collaborative develops and provides tools of this nature. RFG initiated and still contributes to this effort.)
RFG POV: IT executives require a three-to-five year outlook that balances technology trends, operational best practices, and business goals. Immediate and long-range needs need to be plotted, moved, and continuously measured to mitigate immediate and long term needs. While many of these truths are evergreen, it is essential to recognize that the majority of enterprise tools and practices inadequately capture and harmonize the contributing factors. Most enterprise dashboard views evaluate data center performance at a tactical, operational level and identify opportunities for immediate performance improvements. Strategic enterprise dashboard tools tend to build on the data gathered at the tactical level and fail to incorporate evolving strategic business and technology needs. IT executives should incorporate strategic data center optimization planning tools which address the evolving business and technology needs to the mix so that IT can provide the optimum set of services to the business at each milestone.
Tectonic Shifts
Lead Analyst: Cal Braunstein
Bellwether Cisco Systems Inc.'s quarterly results beat expectations while CEO John Chambers opined global business was looking cautiously optimistic. In other system news, IBM Corp. made a series of hardware announcements, including new entry level Power Systems servers that offer better total cost of acquisition (TCA) and total cost of ownership (TCO) than comparable competitive Intel Corp. x86-based servers. Meanwhile, the new 2013 Dice Holdings Inc. Tech Salary Survey finds technology professionals enjoyed the biggest pay raise in a decade last year.
Focal Points:
- Cisco reported its fiscal second quarter revenues rose five percent to $12.1 billion versus the previous year's quarter. Net income on a GAAP basis increased 6.2 percent to $2.7 billion. The company's data center business grew 65 percent compared with the previous year, while its wireless business and service provider video offerings gained 27 and 20 percent, respectively. However, Cisco's core router and switching business did not fare as well, with the router business shrinking six percent and the switching revenues only climbing three percent. EMEA revenues shrank six percent year-over-year while the Americas and Asia Pacific climbed two and three percent, respectively. CEO Chambers warned the overall picture was mixed with parts of Europe remaining very challenging. However, he stated there are early signs of stabilization in government spending and also in probably a little bit over two thirds of Europe. While there is cautious optimism, there is little tangible evidence that Cisco has turned the corner.
- IBM's Systems and Technology Group launched a number of systems and solutions across its product lines, including new PureSystems solutions, on February 5. As part of the announcement was more affordable, more powerful Power Systems servers designed to aggressively take on Dell Inc., Hewlett-Packard Co. (HP), and Oracle Corp. The upgraded servers are based upon the POWER7+ microprocessors and have a starting price as low as $5,947 for the Power Express 710. IBM stated the 710 and 730 are competitively priced against HP's Integrity servers and Oracle's Sparc servers while the PowerLinux 7R1 and 7R2 servers are very aggressively priced to garner market share from x86 servers.
- Dice, a job search site for engineering and technology professionals, recently released its 2013 Tech Salary Survey. Amongst its key findings was that technology salaries saw the biggest year-over-year salary jump in over a decade, with the average salary increasing 5.3 percent. Additionally, 64 percent of 15,049 surveyed in late 2012 are confident they can find favorable new positions, if desired. Scot Melland, CEO of Dice Holdings, stated companies will now have to either pay to recruit or pay to retain and today, companies are doing both for IT professionals. The top reasons for changing jobs were greater compensation (67 percent), better working conditions (47 percent) and more responsibility (36 percent). David Foote, chief analyst at Foote Partners LLC, finds IT jobs have been on a "strong and sustained growth run" since February 2012. By Foote Partners' calculations, January IT employment showed its largest monthly increase in five years. Foote believes the momentum is so powerful that it is likely to continue barring a severe and deep falloff in the general economy or a catastrophic event. Based on Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) data, Foote estimates a gain of 22,100 jobs in January across four IT-related job sectors, whereas the average monthly employment gains from October to December 2012 were 9,700.
RFG POV: While the global economic outlook appears a little brighter than last year, indications are it may not last. Executives will have to carefully manage spending; however, with the need to increase salaries to retain talent this year, extra caution must be undertaken in other spending areas. IT executives should consider leasing IT equipment, software and services for all new acquisitions. This will help to preserve capital while allowing IT to move forward aggressively on innovation, enhancement and transformation projects. RFG studies find 36 to 40 month hardware and software leases are optimum and can be less expensive than purchasing or financing, even over a five year period. Moreover, IBM's new entry level Power Systems servers are another game-changer. An RFG study found that the three-year TCA for similarly configured x86 systems handling the same workload as the POWER7+ systems can be up to 75 percent more expensive while the TCO of the x86 servers can be up to 65 percent more expensive. Furthermore, the cost advantage of the Power Systems could even be greater if one included the cost of development systems, application software and downtime impacts. IT executives should reevaluate its standards for platform selection based upon cost, performance, service levels and workload and not automatically assume that x86 servers are the IT processing answer to all business needs.
Wither Dell?
Lead Analyst: Cal Braunstein
CEO Michael Dell is coordinating a buyout of Dell Inc. for $24.4 billion in the hopes that the company can more effectively go through its transformation if it does not have to deal with reporting results quarterly to fickle investors. Michael Dell's MSD Capital (his investment firm), has teamed with Silver Lake Partners to take the company private. Microsoft Corp. will be assisting in the buyout in the form of a $2 billion loan. If the buyout is successful – which it should be at some price – what does it portend for IT executives and commercial accounts?
To understand where Dell needs to go, one needs to first see where it is. Dell started as a low-cost PC company in the consumer market. It gradually switched to a bifurcated model – PC for consumers and PC and servers for the commercial space, primarily the public, small and medium business (SMB), and large enterprise markets. Over the past six years the company acquired 22 companies – 10 in 2012 alone – and expanded into other hardware components, software and services, including cloud services. But the company has lost its momentum. It lost PC market share and sales in 2012 faster than most of its competitors, which is disastrous for a company that derives more than half of its revenues from end-user computing solutions.
Smartphones and tablets have curtailed the growth of the traditional PC market and Dell's commercial business has not made up for the loss in end-user revenues. In fact, in both businesses Dell is considered a low-cost commodity hardware provider and not a market or thought leader. The company has not fully integrated all of its acquisitions and is struggling to reach its strategic goal of becoming a one-stop shop. The buyout gives the company time to re-think and execute a long-term strategy, reorganize and change its culture. As CEO Meg Whitman at Hewlett-Packard Co. (HP) can attest, a turnaround is a multi-year effort and doing so in public when quarterly results can be volatile is not fun. Thus, the desire by Michael Dell to go private.
While there are a number of challenges that Dell must address, there are two that will make or break the success of the new corporate strategy. The vendor must either exit the end-user computing market or once again become a market leader. It is lacking products in the key current and future end-user markets and it cannot regain its position with just PC solutions to hawk. Secondly, Dell has not been able to transition from a culture of transaction selling to one of relationship sales. If the vendor is to become one of the top one-stop providers in the commercial space, it will have to invest in customer relationship management. This is a massive cultural change that goes to the core of the company. HP has struggled with the clash of this cultural divide since it acquired Compaq in 2002. IBM Corp. took more than 10 years to change its culture. The underlying question will be whether or not CEO Dell, by trade a transactional salesman, can lead the culture shift to succeed with its new corporate vision.
In addition to the above challenges, there are a number of other key issues to be resolved. IT executive relationships with Dell depend on how these shake out.
Assets. Dell will need to decide which assets it has today are worth keeping and which are to be shed. In strong customer relationship management organizations, people are a primary asset. Will Dell address this? Additionally, once it has its strategic vision in place, what additional acquisitions are needed to complete the puzzle? Will the new Dell have the funds to acquire the companies it needs or will the buyout end up choking the firm's ability to compete effectively? Dell recently moved into the equipment leasing space. Will it have the wherewithal to remain?
Business Model. What will Dell's new business model be? It will have to compete with HP, IBM and Oracle Corp. – all of whom are innovators, bring more than commodity products and services to the table, and want to own the complete business relationship with their customers. Each has a different business model. Where will the new Dell position itself?
Business Partners and Channels. Dell will have to re-evaluate how it works with business partners and uses various sales and distribution channels. Dell does have a cloud presence but can it leverage it the way Apple Inc. or Google Inc. do? Can it be a full service provider and still utilize business partners and channels effectively? Without strong business partners and channels Dell will not be able to compete effectively.
Microsoft. Microsoft did not become an owner but a lender to Dell. This will cost the company more than just money. Will it restrict the vendor from providing certain products or solutions?
Processes. Dell needs to revamp its development, operations, and sales processes to be fully integrated and customer relationship based. The customer must come first; not the products or services. This will be a long-term change, which may be agonizing at times.
Technology. Today Dell assembles some products and has the intellectual property (IP) for those products and services that the company acquired. Can it leverage the IP and become recognized as an innovator or will the IP assets wither and the talent depart? Over the past year Dell has been bringing on board the resources to take advantage of the assets. Will the new Dell continue down the same path? If Dell stays in the end-user computing space, will it be able to figure out how to do mobility and social (key components to staying competitive)? If not, will it bite the bullet and exit the business?
The company was at one time the leader in the PC arena. Then it became one of the top players. Now it wants to be a leader in the full-service enterprise space where it is not a top player and is losing momentum.
RFG POV: Dell has a long, tough transformation ahead. By going private it will no longer have to worry about the stock market price but will still have to answer to investors. RFG does not expect the company to pull out of any markets in the near term – although the printing and peripherals business is exposed – but a number of the executives and employees whose visions are out of sync with new direction will depart. In the full-service enterprise space Dell will have to be more than a low-cost provider. It must become a hardware, software, and services innovator, determine its positioning vis-à-vis competitors, make additional acquisitions to fill in the gaps, and spend time and resources building relationships that may not yield near-term revenues. Whether or not the stakeholders will allow the company to spend enough money and time to make the conversion is an open question. The fallback position may be to go back to being a low-cost or custom commodity provider to the commercial market. Moreover, Dell will have to invest in a new end-user computing model, watch its market share shrivel, or quit the space. One thing is for sure – it cannot be all things to all players and must pick its choices carefully. Dell must articulate its strategy to business partners, customers, and employees over the next three to six months or loyalty may falter. In any event, IT executives should expect Dell to provide support and a smooth transition for businesses that are divested, restructured, or sold. IT executives desirous of using Dell as a strategic provider should continue to work closely with Dell, keep abreast of its strategy and roadmaps and factor the knowledge into the corporate decision-making process. Additionally, IT executives should not be surprised or concerned to find the company fails to make the short-list of candidates. There are plenty of options these days.


